The Chengdu University of Technology's State Key Laboratory of Geological Hazard Prevention and Geological Environment Protection conducted a detailed remote sensing analysis of geological disasters triggered by a recent earthquake in Zhongchuan Township, Liuji Township (Liuji Village), and Liuji Township (Yangwa Village). The study revealed widespread co-seismic landslides, particularly in Zhongchuan Township, where 784 landslides occurred covering an area of 137,855 m². Notably, Jintian Village and Caotan Village experienced the largest geological disaster, featuring earthquake-induced landslides and mudflows on a loess tableland. Liuji Village and Yangwa Village also witnessed concentrated seismic-induced landslides, providing valuable insights into the impact of the earthquake on these specific regions.
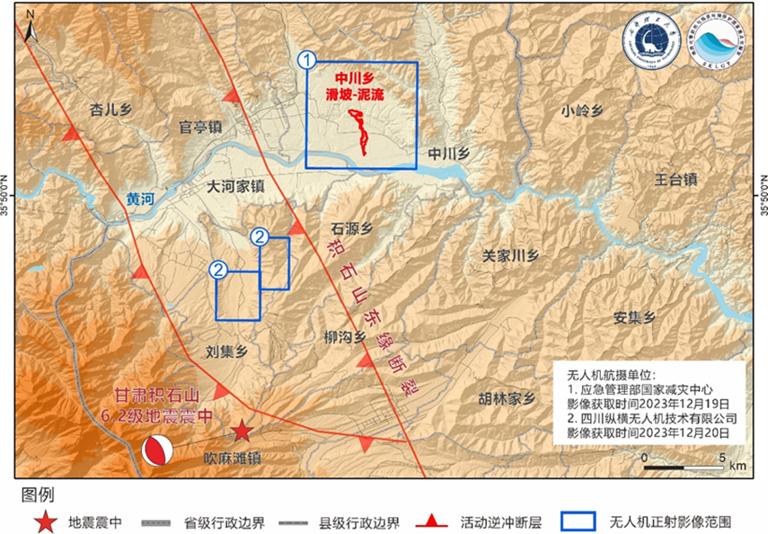
On December 18, 2023, a 6.2-magnitude earthquake struck Jishishan County, Gansu Province. This seismic event triggered multiple geological disasters in the affected area.
Chengdu University of Technology's State Key Laboratory of Geological Hazard Prevention and Geological Environment Protection conducted a detailed remote sensing analysis of geological disasters triggered by a recent earthquake in specific areas. High-resolution unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) images covered Zhongchuan Township, Liuji Township (Liuji Village), and Liuji Township (Yangwa Village).
In Zhongchuan Township (29.58 km²), 784 co-seismic landslides occurred, covering a cumulative area of 137,855 m². The area's flat topography with loess tablelands of coarse silt makes it prone to erosion, especially during concentrated precipitation from July to September. The seismic activity primarily affected ravine sides, causing small soil collapses and landslides in areas such as Xiangyang Village, Pangge Village, and Songjia Hantai vicinity.
Jintian Village and Caotan Village experienced the most significant geological disaster, characterized by earthquake-induced landslides and mudflows on a loess tableland rich in groundwater. The source area covered approximately 110,000 m², with a deposition area extending to about 310,000 m². The mudflow traveled nearly 3 km.
Liuji Township's Liuji Village (5.07 km²) saw 137 co-seismic landslides, totaling 10,212 m². Concentrated seismic-induced landslides occurred in loess terraces and hillsides in specific areas, including Upper Jijia, Lower Jijia, Xuejiapu, and Gaoli Village.
Yangwa Village in Liuji Township (2.49 km²) experienced 137 co-seismic landslides covering 26,655 m², with the largest landslide at 2,243 m². Small, shallow landslides were densely distributed on the west side of Yangwa Village and the north side of Duoluo Gully in terraced farmland and wooded areas, forming a strip-like pattern from northeast to southwest.
Sources:
Chengdu University of Technology
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/Nf3SyGGNW5eNV2ivCB1qXg .
Provided by the IKCEST Disaster Risk Reduction Knowledge Service System
Comment list ( 0 )
