China is tackling the problem of ecological restoration at the national level, seeing it as a vital component of so-called ecological civilization. However, there have been few national-scale reviews of China's ecological restoration for sustainable development initiatives to date. In a paper published on February 23rd, 2023, in National Science Review, scientists guided by Prof. Bojie Fu of the Chinese Academy of Sciences evaluated China’s progress in ecological restoration for sustainable development.
The UN Decade on Ecosystem Restoration, from 2021 through 2030, delivers a rallying call for the protection and revival of ecosystems for the benefit of people and nature, and accordingly, it promotes the timely achievement of the sustainable development goals (SDGs). China is addressing the issue of ecological restoration nationally, as it regards this as an important element of so-called ecological civilization. However, there are few reviews of China's ecological restoration for sustainable development actions at the national scale to date. Researchers led by Prof. Bojie Fu from the Research Center for Eco-Environmental Sciences of the Chinese Academy of Sciences summarized China's progress in ecological restoration for sustainable development in a review published in National Science Review.
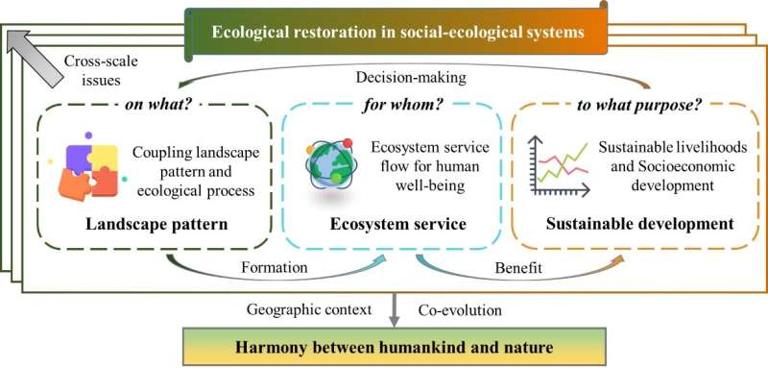
They proposed a "landscape pattern—ecosystem service—sustainable development" co-evolutionary framework to describe landscape-scale ecological restoration and its impact on landscape patterns and ecological processes, ecosystem services for human well-being, sustainable livelihoods and socioeconomic development.
The pattern of China's ecological restoration is becoming more geographically integrated from the strategic pattern of national ecological security to the pattern of major projects to protect and restore major national ecosystems. By 2022, more than 25% of China's territory was covered by areas of ecological red lines, which are believed to powerfully relieve or reverse the ecosystem degradation on ecologically important and sensitive landscapes.
From major function oriented zoning to systematic ecological protection and restoration to towards achievement of the Beautiful China Initiative, The researchers classified three stages of ecosystem services management in China: classification, synergy and integration.
The researchers also held the opinion that the previous programs began as early as in 1978 cannot be regarded as the final word on China's contribution to ecological restoration, which remains work in progress to employ the social-ecological systems approach in the recent and future programs.
Based on quantitative evidence, the researchers found that the past ecological restoration programs in China have greatly influenced ecosystem services, especially carbon sequestration, soil retention and water yield, and their interactions, while some spatiotemporal tradeoff relationships need to be considered.
In addition, the researchers found that there existed local win‒win synergies between ecosystem health and sustainable livelihoods and/or socioeconomic development, while the identification of such win‒win solutions for regional policymaking is still in progress, as benefits and incentives change across scales.
As a geographer, Prof. Fu highlighted the importance of geographical research for integrative ecological protection and restoration. Four important research directions were proposed in a social-ecological system perspective, including: establishing the nature of coupling processes among key components, identifying ecosystem service flows, evaluating social-ecological benefits, and supporting adaptive management for regional sustainable development.
Sources:
Phys.org
https://phys.org/news/2023-04-ecological-sustainable-china.html .
Provided by the IKCEST Disaster Risk Reduction Knowledge Service System
Comment list ( 0 )
